Proteomics is the study of the composition and regulation of proteins at a holistic level, analyzing the composition, expression levels, and modification states to understand the interactions between proteins. Quantitative proteomics is the precise quantitative and qualitative analysis of all proteins expressed in the genome or the target proteins in a mixed system. It is used to explore the protein’s mode of action, mechanisms of regulation and function, as well as the interrelationship between the protein in order to obtain a comprehensive understanding of their different processes, physiological states, and regulatory networks. According to different technical measures, proteonomics can be divided into iTRAQ/TMT proteomics and Label-free proteomics.
ITRAQ (ISoBaric Tag for Relative Absolute Quantitation) and TMT (Tandem Mass Tags) are isotope-labeled quantitation technologies of polypeptides developed in vitro by AB Sciex and Thermo Fisher respectively. The iTRAQ technique specifically labels the amino group of the peptide by a 4-plex or 8-plex. Then, an LC-MS/MS analysis is performed to simultaneously compare the relative expression of proteins in different samples. However, TMT isotopes are labeled with 2-plex, 6-plex, 10-plex, and 16-plex. Both iTRAQ and TMT are classical high-throughput screening techniques in quantitative proteomics, based on similar principles.
Label-free proteomics is a non-isotope labeled quantitative proteomic independent of isotope labeling, which is used for mass spectrometry of enzymatic hydrolyzed peptides of proteins by LC-MS/MS. It overcomes the disadvantages of traditional isotope labeling, yielding a high sample concentration and less pretreatment which can retain more original information of the sample. The coverage of low abundance polypeptides is also higher. Label-free proteomics can detect large samples without the limitation of marker kits.
Applications
- Basic Medicine, Clinical Diagnosis: Biomarkers, disease mechanisms, personalized treatment, etc.
- Biomedicine: Drug action mechanisms, efficacy evaluation, drug development, etc.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Stress resistance mechanisms, growth and development mechanisms, breeding and protection, etc.
- Animal Husbandry: Meat and milk quality, pathogenic mechanisms, etc.
- Food Nutrition: Optimization of food storage conditions, quality identification, food safety monitoring, etc.
- Bioenergy and Environmental Science: Fermentation process optimization, biofuel production, environmental risk assessment, etc.
Competitive Advantages
| TMT/iTRAQ | Label-free |
|---|---|
| 2-16 Plex Isotope Label: 8 groups of samples (iTRAQ) or 16 groups of samples (TMT) can be labeled simultaneously in one experiment. | Low-Cost Experiment: No expensive isotope labeling. |
| Unlimited Sample Type: Label a variety of animal, plant, microbial, clinical, bodily fluid, or cellular samples. | Close To The Original State: Less operation on the sample. |
| Accurate Quantification, Good Repeatability: Samples of the same batch are processed uniformly, which reduces sample processing and experimental error. | Unlimited Sample Conditions: Overcome the disadvantages of quantitative labels by analyzing multiple samples. |
| High Coverage: Low detection limit and low abundance proteins can be detected. | Flexible: Suitable for detecting large samples. |
Quantitative Proteomics Work Flow
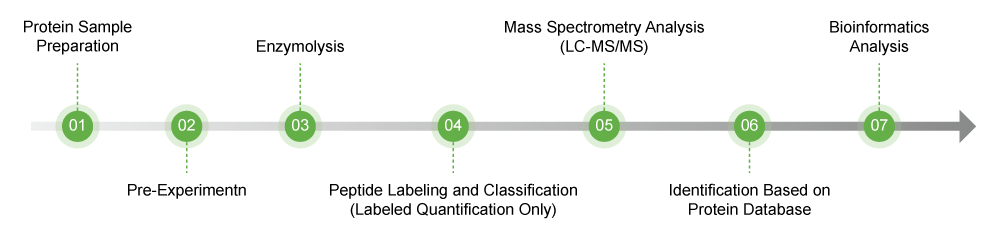
Quantitative Proteomics Work Flow
| Sample Type | Sample Requirements | Platform | Price | Turnaround Time | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell | ≥107 | Thermo Orbitrap Fusion Lumos | Inquire | Inquire |
|
| Tissue | Animal tissue ≥100mg, plant tissue ≥100mg, microorganism ≥20mg | ||||
| Protein extracting solution | ≥100µg | ||||
| Bodyfluid | Serum/plasma ≥200µL, urine ≥1ml, saliva/cerebrospinal fluid ≥1ml, tear ≥1ml | ||||
| Exosome | ≥10µL | ||||
| FFPE | ≥0.3 mm * 0.3 mm |
Project Design
The design idea of quantitative proteomics experiments is to compare differential proteins under different treatments or physiological states, to explore the difference of mechanisms. At the same time, it can also provide a theoretical basis for plant stress resistance, breeding protection, meat and dairy products quality, animal disease research, and other fields as well. At least 3 biological replicates are required for each group, and the more biological replicates, the better.
Analysis Item
| Number | Analysis Item | Number | Analysis Item |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data quality control and distribution analysis | 6 | Domain enrichment analysis |
| 2 | Protein quantitative analysis | 7 | PPI network analysis |
| 3 | Differential protein expression analysis | 8 | Protein cluster analysis |
| 4 | GO enrichment analysis | 9 | Personalized analysis |
| 5 | KEGG pathway analysis | 10 | Integrative analysis of multiomics |
Data Analysis
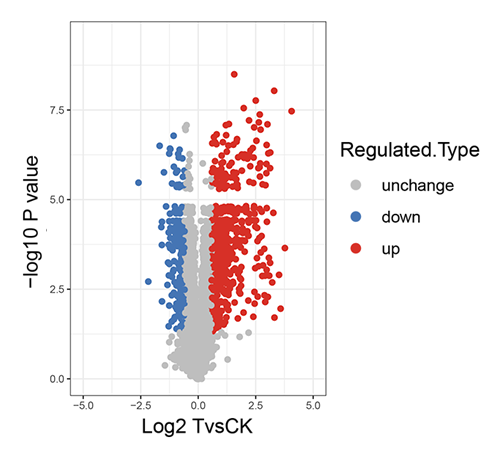
Differential Protein Volcano Plot
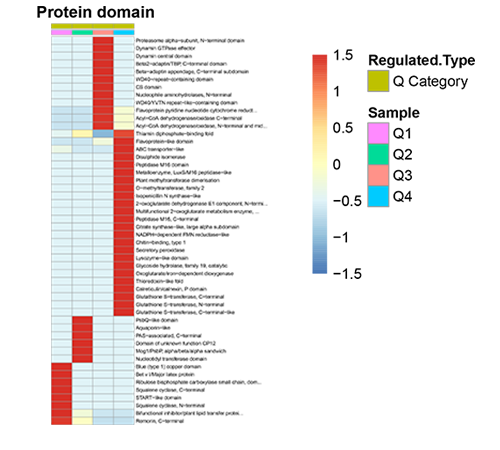
Protein Domain Cluster Heatmap
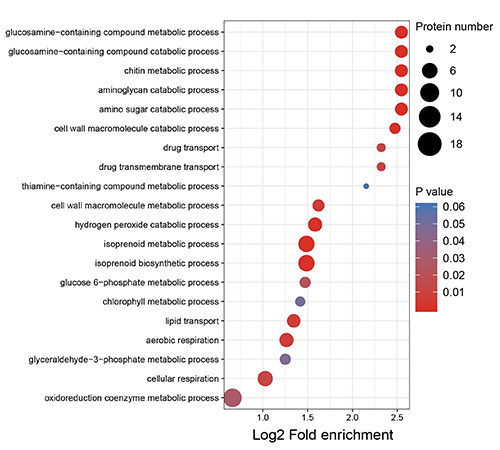
GO Enrichment Bubble Plot
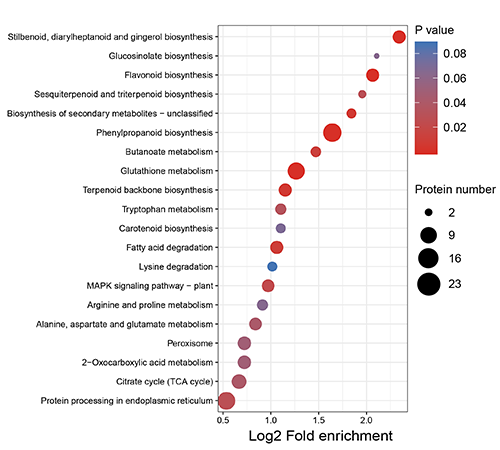
KEGG Pathway Enrichment Plot
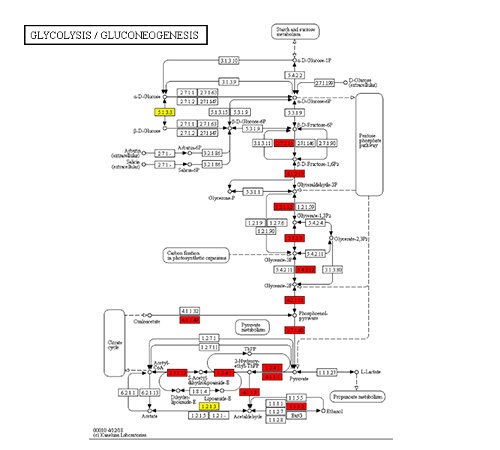
KEGG Metabolic Pathway
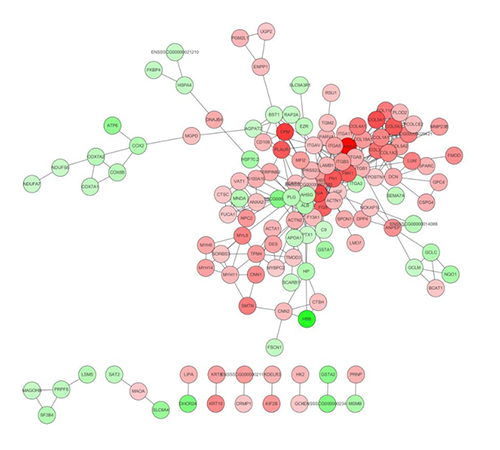
PPI Network

